Python Data Structures — Lists, Tuples, and Dictionaries
Python Data Structures help you store and organize data efficiently. The three most commonly used data structures are Lists, Tuples, and Dictionaries. Below is a clear overview with examples and mini challenges to practice your skills.
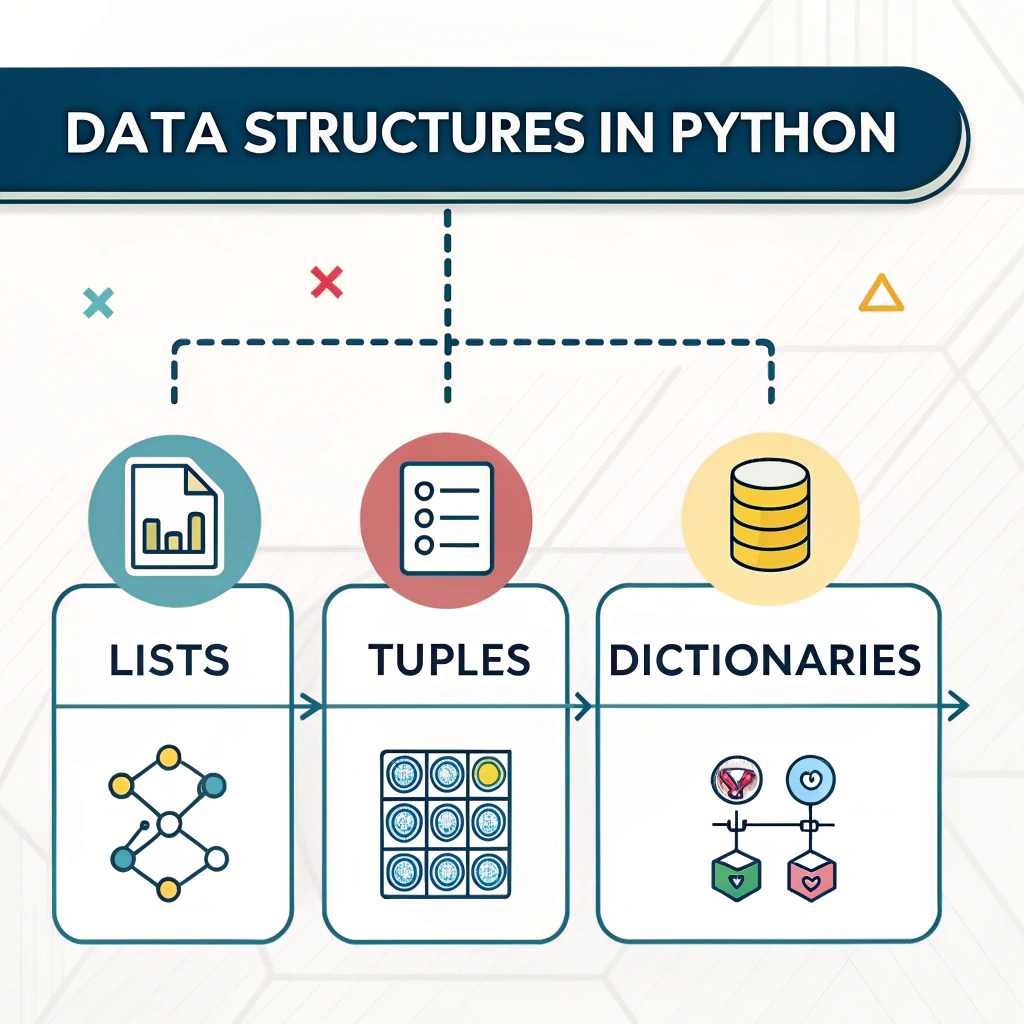
What Are Data Structures?
A data structure is a way of organizing and storing data so it can be used efficiently. Python has several built-in data structures, but the most common ones are:
- Lists — Ordered and mutable collections
- Tuples — Ordered but immutable collections
- Dictionaries — Key-value pairs, unordered and mutable
1. Python Data Structures: Lists — The All-Rounder
A list is an ordered, mutable collection that can hold numbers, strings, or even other lists.
Creating a List
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "mango", "orange"]
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
mixed = [1, "hello", 3.5, True]
Accessing Elements
print(fruits[0]) # apple
print(fruits[2]) # mango
Modifying Lists
fruits[1] = "grape"
Adding Items
fruits.append("cherry") # Add at the end
fruits.insert(1, "kiwi") # Add at specific index
fruits.extend(["pineapple", "pear"]) # Add multiple items
Removing Items
fruits.remove("apple") # Remove by value
fruits.pop(0) # Remove by index
fruits.clear() # Remove all items
Looping Through a List
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
Useful Functions
len(list)→ Count itemssum(list)→ Sum of numberssorted(list)→ Sort items
Mini Challenge
Write a program that takes 5 numbers from the user and prints:
- Largest number
- Smallest number
- Sum of all numbers
2. Python Data Structures: Tuples — The Unchangeable List
A tuple is ordered like a list but immutable — its contents cannot be changed.
Creating a Tuple
colors = ("red", "green", "blue")
Accessing Elements
print(colors[0]) # red
print(colors[2]) # blue
You Cannot Modify a Tuple
# colors[1] = "yellow" # ❌ Error
Looping Through a Tuple
for color in colors:
print(color)
Tuple Operations
- Concatenation:
(1,2) + (3,4)→(1,2,3,4) - Repetition:
("Hi",) * 3→('Hi', 'Hi', 'Hi') - Length:
len(colors)→3
Mini Challenge
Create a tuple with your 3 favorite movies and print them one by one.
3. Python Data Structures: Dictionaries — Key-Value Powerhouse
A dictionary stores data in key-value pairs. It is unordered and mutable.
Creating a Dictionary
student = {
"name": "Alice",
"age": 20,
"course": "Python"
}
Accessing Values
print(student["name"]) # Alice
print(student.get("course")) # Python
Adding or Updating Items
student["age"] = 21 # Update
student["city"] = "New York" # Add
Removing Items
student.pop("course") # Remove by key
del student["city"] # Remove key
student.clear() # Remove all items
Looping Through a Dictionary
for key, value in student.items():
print(key, ":", value)
Useful Methods
keys()→ List all keysvalues()→ List all valuesitems()→ List all key-value pairsupdate()→ Add multiple items
Mini Challenge
Create a dictionary for a book with keys: Title, Author, Price. Print all details neatly.
Combining Data Structures
You can nest lists, tuples, and dictionaries for advanced data storage.
Example: List of Dictionaries
students = [
{"name": "Alice", "marks": 85},
{"name": "Bob", "marks": 78},
{"name": "Charlie", "marks": 92}
]
for s in students:
print(s["name"], "scored", s["marks"])
Output:
Alice scored 85
Bob scored 78
Charlie scored 92
Practice Tasks
- Create a list of 5 fruits and remove the 3rd one.
- Store a tuple of 3 countries and print them using a loop.
- Create a dictionary of 3 students (name: marks) and print each name with marks.
- Write a program that takes a list of numbers and prints only the even ones.
- Bonus: Make a mini phonebook using a dictionary (name as key, number as value).
- Extra Practice: Combine a list, tuple, and dictionary in a single program to store and display different types of data.
Python Data Structures help you store and organize data efficiently. The three most commonly used data structures are Lists, Tuples, and Dictionaries. Below is a clear overview with examples and mini challenges to practice your skills.
Summary of Key Skills
- Use Lists, Tuples, and Dictionaries
- Add, remove, and access items
- Loop through data structures
- Combine them for complex storage
These are fundamental skills for Python programmers, enabling you to build apps like contact books, student databases, and small games.